Answer:
7.43 × 10²⁴ m⁻³
Step-by-step explanation:
Data provided in the question:
Conductivity of a semiconductor specimen, σ = 2.8 × 10⁴ (Ω-m)⁻¹
Electron concentration, n = 2.9 × 10²² m⁻³
Electron mobility,
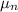 = 0.14 m²/V-s
= 0.14 m²/V-s
Hole mobility,
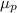 = 0.023 m²/V-s
= 0.023 m²/V-s
Now,
σ =
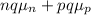
or
σ =
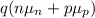
here,
q is the charge on electron = 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C
p is the hole density
thus,
2.8 × 10⁴ = 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹( 2.9 × 10²² × 0.14 + p × 0.023 )
or
1.75 × 10²³ = 0.406 × 10²² + 0.023p
or
17.094 × 10²² = 0.023p
or
p = 743.217 × 10²²
or
p = 7.43 × 10²⁴ m⁻³