Answer:
The standard cell potential at 25 ∘C for the reaction is 2.72 Volts.
Step-by-step explanation:
Δ°G = Δ°H - TΔ°S (Gibb's equation)
Δ°G = Gibbs free energy
Δ°H = Enthalpy of the reaction at temperature T
Δ°S = Entropy of the reaction at temperature T

n = number of electrons transferred
F = Faraday's constant = 96500 C
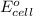 = standard electrode potential of the cell
= standard electrode potential of the cell
We have:
Δ°H = -829 kJ = -829000 J
Δ°S = -367 J/K
T = 25 C = 298.15 K
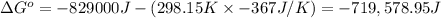
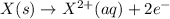
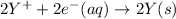
n = 2
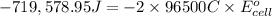
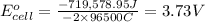
The standard cell potential at 25 ∘C for the reaction is 2.72 Volts.