Answer:
The work function ϕ of the metal = 53.4196 x 10⁻¹⁶ J
Step-by-step explanation:
When light is incident on a photoelectric material like metal, photoelectrons are emitted from the surface of the metal. This process is called photoelectric effect.
The relationship between the maximum kinetic energy (
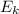 ) of the photoelectrons to the frequency of the absorbed photons (f) and the threshold frequency (f₀) of the photoemissive metal surface is:
) of the photoelectrons to the frequency of the absorbed photons (f) and the threshold frequency (f₀) of the photoemissive metal surface is:
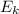 = h(f − f₀)
= h(f − f₀)
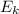 = hf - hf₀
= hf - hf₀
E is the energy of the absorbed photons: E = hf
ϕ is the work function of the surface: ϕ = hf₀
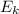 = E - ϕ
= E - ϕ
Frequency f = 8.12×10¹⁸ Hz
Maximum kinetic energy
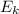 = 4.16×10⁻¹⁷ J
= 4.16×10⁻¹⁷ J
Speed of light c = 3 x 10⁸ m/s
Planck's constant h = 6.63 × 10⁻³⁴ Js
E = hf = 6.63 × 10⁻³⁴ x 8.12×10¹⁸
E = 53.8356 x 10⁻¹⁶ J
from
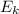 = E - ϕ ;
= E - ϕ ;
ϕ = E -
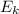
ϕ = 53.8356 x 10⁻¹⁶ - 4.16×10⁻¹⁷
ϕ = 53.4196 x 10⁻¹⁶ J
The work function of the metal ϕ = 53.4196 x 10⁻¹⁶ J