Answer:
2d
Step-by-step explanation:
For any instance equivalent force acting on the body is
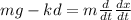
Where
m is the mass of the object
k is the force constant of the spring
d is the extension in the spring
and
d/dt(dx/dt)= is the acceleration of the object
solving the above equation we get
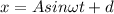
where
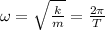
A is the amplitude of oscillation from the mean position.
k= spring constant , T= time period
Here we are assuming that at t=T/4
x= 0 since, no extension in the spring
then
A=- d
Hence
x=- d sin wt + d
now, x is maximum when sin wt=- 1
Therefore,
x(maximum)=2d