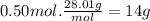Answer:
14 g
Step-by-step explanation:
First, we have to calculate the partial pressure of N₂. We know that the air is 80% nitrogen by volume, which, for a gas mixture, means that the mole fraction of N₂ is 0.80.
We can calculate the partial pressure of N₂ (pN₂) using the following expression:
pN₂ = P . x(N₂)
where,
P is the total pressure
x(N₂) is the mole fraction of N₂
pN₂ = 1.1 atm . 0.80 = 0.88 atm
Then, we can calculate the moles of N₂ using the ideal gas equation.
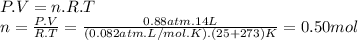
Considering that the molar mass of N₂ is 28.01 g/mol, the mass of N₂ is: