Answer: In that case, consumer need to buy more units of Y and less units of X.
Explanation:
Since we have given that
Marginal utility of X = 10
Marginal utility of Y = 8
Unit price of X = $5
Unit price of Y = $2
So, we know that
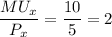
and
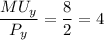
Since
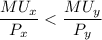
In that case, consumer need to buy more units of Y and less units of X.
So, MU of y becomes lower and MU of x becomes higher until they becomes equal to each other to attain consumer's equilibrium.