Answer:
1.) 9.9
2.) 15.6
Explanation:
1.) Consider triangle AEH
AEH is a right angle triangle as ∠AEH = 90°
AH is the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Applying Pythagorean theorem
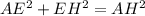
substituting values as given in the question:
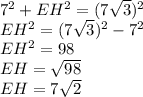
∴ EH≈9.9
2.) Consider triangle CDF
CDF is a right angle triangle as ∠CDF = 90°
CF is the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Applying Pythagorean theorem
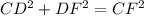
substituting values as given in the question:
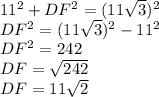
∴ DF≈15.6