Answer:
The margin of error is multiplied by
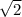
Explanation:
margin of error (ME) from the mean can be calculated using the formula
ME=
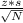 where
where
- z is the corresponding statistic of the given confidence level
- s is the standard deviation of the sample (or of the population if it is known)
Since margin of error is proportional with inverse of
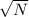 ,
,
if we cut the sample size in half, the margin of error is multiplied by
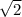 .
.