Answer:
The volume occupied by the gas at a pressure of 2.90 atm = 140L
Step-by-step explanation:
Since we are assuming ideal behavior, the gas equation is:
pV = nRT
where, p is the pressure
V is the volume
R is the universal gas constant
T is the temperature
The temperature is constant. We can use the Boyle's Law:
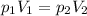
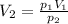 -----(1)
-----(1)
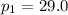 atm
atm
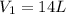
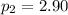 atm
atm
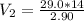 =
=
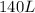
Therefore, at the same temperature, the volume occupied by the gas at a pressure of 2.90 atm is 140L.