Answer:
1.62 %
Step-by-step explanation:
Percent ionization can be expressed as:
[H⁺]/[HA] * 100%
We're already given [HA], the molar concentration of lactic acid (0.120 M), so now we need to calculate [H⁺].
To do that we can use the Henderson-Hasselbach equation:
pH = pKa + log [A⁻]/[HA]
The pKa of lactic acid is 3.86, and we're given the concentrations of lactic acid and its salt (sodium lactate):
pH = 3.86 + log [8.5x10⁻³]/[0.120]
pH = 2.71 = -log [H⁺]
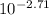 = [H⁺]
= [H⁺]
[H⁺] = 1.95x10⁻³M
Finally we calculate the percent ionization:
1.95x10⁻³ / 0.120 = 1.62 %