Answer:
37.5
Step-by-step explanation:
Acording to the the Hardy-Weinberg equation:
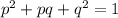
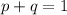
Where p is the frequency of the dominant allele "T", and q is the frequency of the recessive allele "t".
Therefore, p^2 is the frequency of the dominant homozygous genotype "TT", q^2 is the frequency of the recessive homozygous genotype "tt" and
2pq is the frequency of the heterozygous genotypes "Tt" and "tT".
Since 1 in 16 individuals have inherited two recessive alleles (tt) and have the disease:
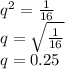
Thus, the fraction of heterozygous carriers of the studius toxicosis allele in the population is given by:
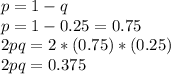
37.5 percent of the population are heterozygous carriers