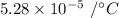Answer:
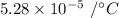
Step-by-step explanation:
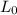 = Original length of rod
= Original length of rod
 = Coefficient of linear expansion =
= Coefficient of linear expansion =
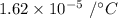
Initial temperature = 16°C
Final temperature = 260°C
Change in length of a Steel is given by
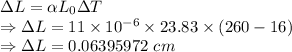
Change in material rod length will be
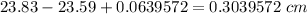
The coefficient of thermal expansion is given by
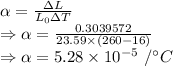
The coefficient of thermal expansion for the material is