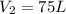Answer:
75 L
Step-by-step explanation:
We assume that the gas in the container is an ideal gas, which is governed by the ideal gas equation : PV = nRT , where P is the pressure of the gas, V is the volume of the container, n is the number of mols of the gas, R is the universal gas constant and T is the temperature of the gas.
Here, R is a universal constant with a value of ≈ 8.314 J/mol-K. Also, given that temperature (T) is maintained constant. And since the container is closed, there is no exchange of the gas between the container and the surroundings, thus keeping the number of mols (n) of the gas constant. Hence, in the ideal gas equation, right hand side, i.e, nRT is a constant.
Initially the equation is:
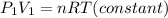
Finally, the equation is:
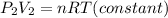
Since, nRT is a constant,
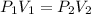
It is given that,
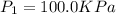 ,
,
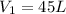 and
and
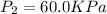 .
.
Therefore, 100x45 = 60 x
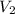 ⇒
⇒