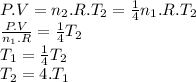Answer:
e. T₂= 4T₁
Step-by-step explanation:
Initially, we have a number of moles (n₁) a gas sample at a certain pressure (P), temperature (T₁) and volume (V). We can relate these variables through the ideal gas equation.
P . V = n₁ . R . T₁
where,
R is the ideal gas constant
We can rearrange this equation like:
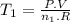
If only one fourth of the initial molecules remain n₂ = 1/4 n₁. The new temperature (T₂) assuming pressure and temperature remain constant is: