Answer:
Answered
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The magnitude of the magnetic flux through the coil before it is rotated is,
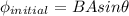
=BAsin90° = BA
therefore, the magnitude of the magnetic flux= BA
b) The magnitude of the magnetic flux through the coil after it is rotated is, Ф_final = BAsinθ
= BA sin0= 0
therefore, the magnitude of magnetic flux through the coil after it is rotated is, zero.
c) The magnitude of the average emf induced in the coil is,
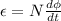
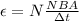
because Ф = BA