Answer:
a) Alternative hypothesis should be one sided. Because Null and Alternative hypotheses are:
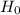 : μ=2.66 dyne-cm.
: μ=2.66 dyne-cm.
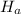 : μ<2.66 dyne-cm.
: μ<2.66 dyne-cm.
b) the hypothesis that mean adhesion is at least 2.66 dyne-cm is true
Explanation:
Let μ be the mean adhesion in dyne-cm.
a)
Null and alternative hypotheses are:
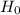 : μ=2.66 dyne-cm.
: μ=2.66 dyne-cm.
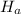 : μ<2.66 dyne-cm.
: μ<2.66 dyne-cm.
b)
First we need to calculate test statistic and then the p-value of it.
test statistic of sample mean can be calculated as follows:
t=
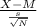 where
where
- M is the mean adhesion assumed under null hypothesis (2.66 dyne-cm)
- s is the standard deviation known (0.7 dyne-cm_2)
Sample mean is the average of 2.69, 5.76, 2.67, 1.62 and 4.12 dyne-cm, that is
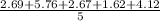 ≈ 3.37
≈ 3.37
using the numbers we get
t=
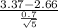 ≈ 2.27
≈ 2.27
The p-value is ≈ 0.043. Taking significance level as 0.05, we can conlude that sample proportion is significantly higher than 2.66 dyne-cm.
Thus, according to the sample the hypothesis that mean adhesion is at least 2.66 dyne-cm is true