Step-by-step explanation:
The heat gained by the solution = q
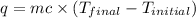
where,
q = heat gained = ?
c = specific heat of solution=
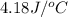
Mass of the solution(m) = mass of water + mass of calcium chloride
Mass of water = ?
Volume of water = 50.00 mL
Density of water = 1.00 g/mL
Mass = Density × Volume
m = 1.00 g/mL × 50.00 mL = 50.00 g
Mass of the solution (m) = 50.00 g + 4.51 g =54.51 g
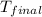 = final temperature =
= final temperature =
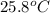
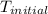 = initial temperature =
= initial temperature =
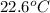
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
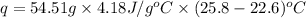
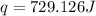
The heat gained by the solution is 729.126 J.
Heat energy released during the reaction = q'
q' = -q ( law of conservation of energy)
q' = -729.126 J
The heat energy released during the reaction is -729.126 J.
Moles of calcium chloride, n =
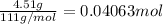
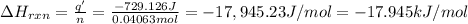
The ΔH of the reaction is -17.945 kJ/mol.