Answer:
The ΔS° for this reaction is -626.22 J/K.
Step-by-step explanation:
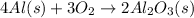
The equation used to calculate ΔS° is of a reaction is:
![\Delta S^o_(rxn)=\sum [n* \Delta S^o_f(product)]-\sum [n* \Delta S^o_f(reactant)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/8t0rsktsi0mjos5omr14voiafivcsdaqe8.png)
The equation for the enthalpy change of the above reaction is:
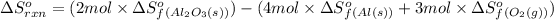
We are given:
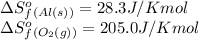
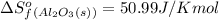
Putting values in above equation, we get:
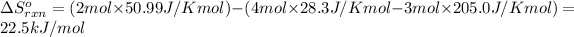
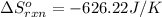
The ΔS° for this reaction is -626.22 J/K.