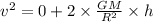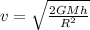Answer:
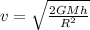
Step-by-step explanation:
mass of object = m
Mass of planet = M
Radius of planet = R
Height = h
Let the speed of the object as it hits the earth's surface is v.
the value of acceleration due to gravity
g = G M / R^2
where, g is the universal gravitational constant.
Use third equation of motion
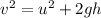
where, u is the initial velocity which is equal to zero.
So,