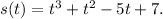Answer: The required position function is
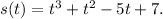
Step-by-step explanation: Given that a particle moves in a straight line and has acceleration given by
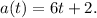
The initial velocity of the particle is v(0) = −5 cm/s and its initial displacement is s(0) = 7 cm.
We are to find the position function s(t).
We know that the acceleration function a(t) is the derivative of the velocity function v(t). So,

Also, the velocity function v(t) is the derivative of the position function s(t). So,

From equation (i), we get
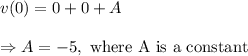
and from equation (ii), we get
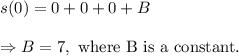
Substituting the values of A and B in equation (ii), we get
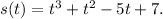
Thus, the required position function is