Answer:
The amount of hydrogen gas collected will be 0.5468 g
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
Vapor pressure of water = 44.6 torr = 44.6 mm Hg
Total vapor pressure = 855 mm Hg
Vapor pressure of hydrogen gas = Total vapor pressure - Vapor pressure of water = (855 - 44.6) mmHg = 810.4 mmHg
To calculate the amount of hydrogen gas collected, we use the equation given by ideal gas which follows:
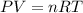
where,
P = pressure of the gas = 810.4 mmHg
V = Volume of the gas = 6.50 L
T = Temperature of the gas =
![36^oC=[36+273]K=309K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/6c2ijfqh6voqu49lpk9xp94bilt6j94nck.png)
R = Gas constant =
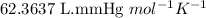
n = number of moles of hydrogen gas = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
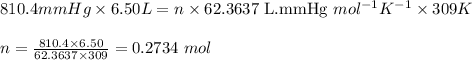
To calculate the mass from given number of moles, we use the equation:
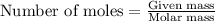
Moles of hydrogen gas = 0.2734 moles
Molar mass of hydrogen gas = 2 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
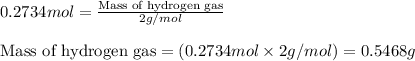
Hence, the amount of hydrogen gas collected will be 0.5468 g