Answer:
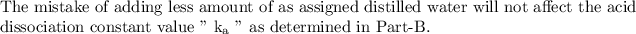
Step-by-step explanation:
The quantitative measurement of strength of an acid in solution named as acid dissociation constant
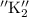 . For acid-base titration this analysis is preferred and it is equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction.
. For acid-base titration this analysis is preferred and it is equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction.
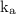 is constant despite of concentration, for example it measures breakdown of an acid into the conjugate base
is constant despite of concentration, for example it measures breakdown of an acid into the conjugate base
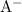 and hydrogen ion
and hydrogen ion
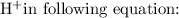
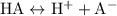
![\underline{\mathbf{k}}_{\mathbf{a}}=\frac{\left[\mathrm{H}^(+)\right] \cdot[\mathrm{A}]}{[\mathrm{HA}]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/vd3p56wk0oqgs0ehobievokmlhlfi9ipg3.png)
Here amount of
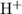 produced is proportional to the amount of H-A from which started. Therefore amount of
produced is proportional to the amount of H-A from which started. Therefore amount of
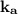 remain constant for a particular acid despite a change in concentration of both acid or base with which it is reacting.
remain constant for a particular acid despite a change in concentration of both acid or base with which it is reacting.