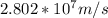To solve this problem it is necessary to resort to the energy conservation equations, both kinetic and electrical.
By Coulomb's law, electrical energy is defined as
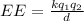
Where,
EE = Electrostatic potential energy
q= charge
d = distance between the charged particles
k = Coulomb's law constant
While kinetic energy is defined as
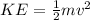
Where,
m= mass
v = velocity
There by conservation of energy we have that
EE= KE
There is not Initial kinetic energy, then
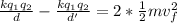
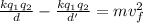
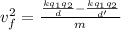
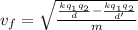
Replacing with our values we have,
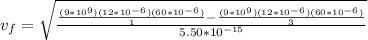
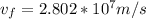
Therefore the speed of particle B at the instat when the particles are 3m apart is