Answer:
0.036 M of
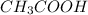
Step-by-step explanation:
It is an example of acid-base neutralization reaction.
KOH +
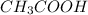 ---->
---->
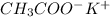 +
+
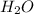
Base Acid Salt
When two component react then the number of moles of both the component should be same, therefore the number of moles and acids and bases should be the same in the following .
Molarity=
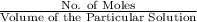
No.of moles= Molarity × Volume of the Particular Solution
Therefore,
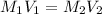 ------------------------------(1)
------------------------------(1)
where
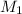 = Molarity of Acid
= Molarity of Acid
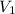 = Volume of Acid
= Volume of Acid
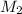 = Molarity of Base
= Molarity of Base
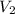 = Volume of Base
= Volume of Base
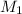 =0.3330 M
=0.3330 M
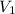 =10.62 mL
=10.62 mL
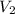 =98.2 mL
=98.2 mL
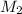 =??(in M)
=??(in M)
Plugging in Equation 1,
0.3330 × 10.62 =
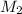 × 98.2
× 98.2
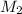 =
=
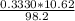
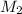 =0.036 M
=0.036 M