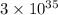Answer:
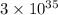
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced chemical equation will be:
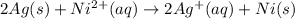
Here Ag undergoes oxidation by loss of electrons, thus act as anode. Nickel undergoes reduction by gain of electrons and thus act as cathode.
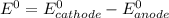
Where both
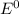 are standard reduction potentials.
are standard reduction potentials.
![E^0_([Ag^(+)/Mg])=+0.80V](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/vif8rpaujva9t67bfg2t20jbbdth22mmng.png)
![E^0_([Ni^(2+)/Ni])=-0.25V](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/htbuui1xluevl0gv5nikvdy29jfa9xkzuz.png)
![E^0=E^0_([Ni^(2+)/Ni])- E^0_([Ag^(+)/Ag])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/qg45w3wxfbynl78eeuq92l6ii1c7ys20po.png)
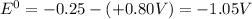
The standard emf of a cell is related to Gibbs free energy by following relation:

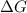 = gibbs free energy
= gibbs free energy
n= no of electrons gained or lost =?
F= faraday's constant
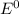 = standard emf
= standard emf
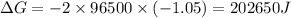
The Gibbs free energy is related to equilibrium constant by following relation:
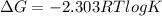
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/Kmol
T = temperature in kelvin =
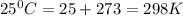
K = equilibrium constant
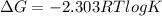
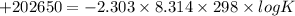
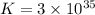
Thus the value of the equilibrium constant at
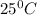 is
is