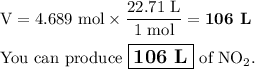Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
We will need a balanced chemical equation with molar masses and volumes, so, let's gather all the information in one place.
MV/L: 22.71
M_r: 63.55
Cu + 4HNO₃ ⟶ Cu(NO₃)₂ + 2H₂O + 2NO₂
m/g: 149
(a) Moles of Cu
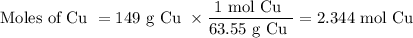
(b) Moles of NO₂
The molar ratio is 2 mol NO₂:1 mol Cu
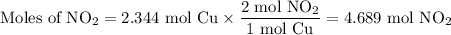
(c) Volume of NO₂
The volume of 1 mol of an ideal gas at STP (0 °C and 1 bar) is 22.71 L.