Answer:
When the denominator is an irrational number in order to make the denominator a rational number we rationalize the denominator.
Explanation:
For example,
 (here the denominator is an irrational number)
(here the denominator is an irrational number)
Multiply the numerator and denominator by
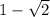
We get
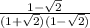
Here (1+\sqrt{2})(1-\sqrt{2}) = -1
Thus we get
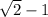
Here the denominator has become a rational number.
When we are isolating a variable we are only taking the required variables to one side thus it doesn't require rationalization.
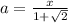
Then we can say,
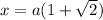
No rationalisation required