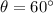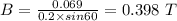Answer:
(a) 0.345 T
(b) 0.389 T
Solution:
As per the question:
Hall emf,
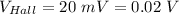
Magnetic Field, B = 0.10 T
Hall emf,
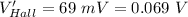
Now,
Drift velocity,
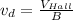
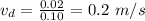
Now, the expression for the electric field is given by:
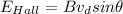 (1)
(1)
And

Thus eqn (1) becomes
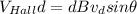
where
d = distance
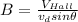 (2)
(2)
(a) When
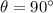
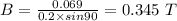
(b) When