Answer:
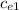 = 0.331 J / g ° C
= 0.331 J / g ° C
Step-by-step explanation:
We have a calorimetry exercise where all the heat yielded by one of the components is absorbed by the other.
Heat ceded Qh = m1 ce1 (
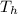 -
-
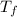 )
)
Heat absorbed Qc = m2 ce2 (
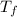 - T₀)
- T₀)
Body 1 is metal and body 2 is water . Where m are the masses of the two bodies, ce their specific heat and T the temperatures
Qh = Qc
m₁
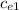 (
(
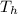 -
-
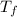 ) = m₂
) = m₂
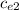 (
(
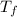 - T₀)
- T₀)
we clear the specific heat of the metal
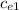 = m₂
= m₂
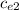 (
(
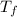 - T₀) / (m₁ (
- T₀) / (m₁ (
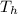 -
-
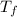 ))
))
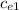 = 50.00 4.184 (20.15 -10.79) / (75.00 (99.0-20.15))
= 50.00 4.184 (20.15 -10.79) / (75.00 (99.0-20.15))
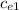 = 209.2 (9.36) / (75 78.85)
= 209.2 (9.36) / (75 78.85)
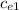 = 1958.11 / 5913.75
= 1958.11 / 5913.75
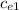 = 0.331 J / g ° C
= 0.331 J / g ° C