Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Let x₀ be the amplitude , ω be the angular velocity
velocity at displacement x ,
v = ω
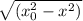
at
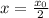
v = ω [
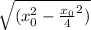
v² = ω² x
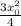
1/2 m v²
= 3/8 m x ω²x₀²
Total energy = 1/2 m ω²x₀²
Kinetic energy as fraction of total energy
= 3/8 m x ω²x₀² x 2 / m ω²x₀²
= 3 / 4
Fraction of potential energy
= 1 - 3/4
1/4
c )
Half kinetic = half potential energy
= 1/4 m ω²x₀²
1/2 m ω²( x₀²- x ² )
x₀²/2 = x₀²- x ²
x² = x₀²/2
x = x₀/√2