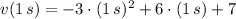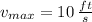Answer:
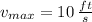 at
at
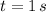 .
.
Explanation:
The velocity function is found by deriving once:
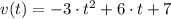
The acceleration function is determined by deriving again:
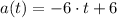
The critical point of the velocity function is computed by equalizing the acceleration function to zero and clearing t:
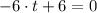
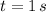
The Second Derivative Test is done by deriving the acceleration function and checking the critical point hereafter:
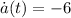
Which indicates that critical point leads to maximum velocity, which is: