To solve this problem it is necessary the concepts related to radiant energy emitted by the bodies and their method to find it through the Blackbody radiation functions table.
From the given values we have that the temperature is 2500K and that the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum extends from
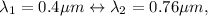
With the wavelength and temperature we can find the relationship
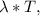 then
then
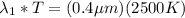
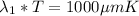
From blackbody radiation functions table (attached) we have that
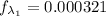
In the case of the second wave
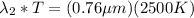
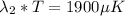
From the table,
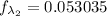
We can calculate the fraction of radian energy emitted by,
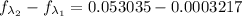
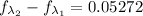
Therefore about 5% of the radiation emitted by the filament of the lightbulb falls in the visible range.