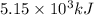Answer:
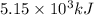
Explanation:-
As we know heat released will be same as heat absorbed by the calorimeter
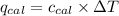
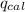 = Heat gained by bomb calorimeter
= Heat gained by bomb calorimeter
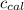 =Heat capacity of bomb calorimeter=12.66 kJ/°C
=Heat capacity of bomb calorimeter=12.66 kJ/°C
Change in temperature = ΔT=
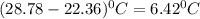
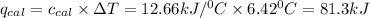
Let the heat released during reaction be q.
q = Heat released = 81.3 kJ
1.800 g of octane releases = 81.3 kJ of heat
Moles of octane =
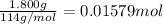
0.01579 moles of octane releases 81.3 kJ of heat
1 mole of octane releases =
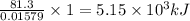 of heat
of heat
Thus
 for the combustion of one mole of octane is
for the combustion of one mole of octane is