Answer:
a)
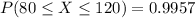
b)
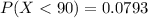
c)
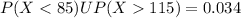
d)
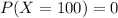
Explanation:
1) Notation and data given
n= 200 represent the total tosses
p(head)=p(tails)=1/2=0.5 if is a fair coin
The experiment on this case is tossing 200 times a coin
We can calculate np=200*0.5=100>10 and nq=n(1-p)=200*(1-0.5)=100>10
So then since np>10 and nq>10 we can use the approximation normal to the binomial distribution.
Let X our random variable who represents "the number of heads obtained in 200 tosses from a fair coin". This random variable X follows a normal distribution. And since we have all the conditions satisfied we can calculate the mean and the deviation for the normal distribution
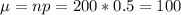
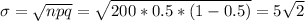
Since X follows a normal distribution we can standarize on this way
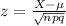
And z is distributed normal with mean= and deviation =1.
This z score would be useful in order to calculate the probabilities required.
2) Part a
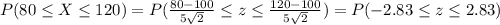
Using properties from the normal distribution we have this
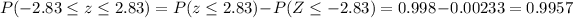
3) Part b
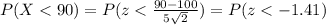
And using a the normal standard distribution table or excel we find that:
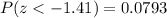
4) Part c
Since the events
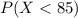 and
and
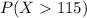 are independent, so we can find the probability like this
are independent, so we can find the probability like this
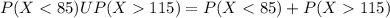
So we can find individually the probabilities like this:
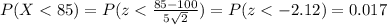
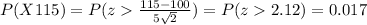
So then:
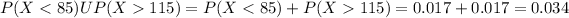
5) Part d
If we use the normal approximation since the area below the curve for a point is not defined. Then the probability P(X=100) would be 0.