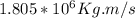To solve the problem it is necessary to apply the concepts related to Conservation of linear Moment.
The expression that defines the linear momentum is expressed as
P=mv
Where,
m=mass
v= velocity
According to our data we have to
v=10m/s
d=0.05m
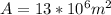
Volume
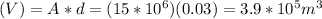
t = 3hours=10800s
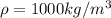
From the given data we can calculate the volume of rain for 5 seconds
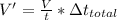
Where,
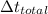 It is the period of time we want to calculate total rainfall, that is
It is the period of time we want to calculate total rainfall, that is
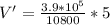
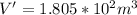
Through water density we can now calculate the mass that fell during the 5 seconds:
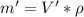
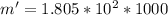
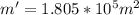
Now applying the prevailing equation given we have to
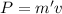
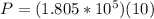
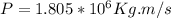
Therefore the momentum of the rain that falls in five seconds is