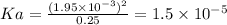Answer:
Ka = 1.5 × 10⁻⁵
Step-by-step explanation:
Butyric acid is a weak acid that ionizes according to the following equation:
CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-COOH(aq) ⇄ CH₃-CH₂-CH₂-COO⁻(aq) + H⁺(aq)
We can find the value of the acid dissociation constant (Ka) using the following expression:
![Ka=([H^(+)]^(2) )/(Ca)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/h8putk6t3my20piw8pj0rgzgutt4e1huda.png)
where
[H⁺] is the molar concentration of H⁺
Ca is the initial molar concentration of the acid
We can find [H⁺] from the pH.
pH = -log [H⁺]
[H⁺] = antilog -pH = antilog -2.71 = 1.95 × 10⁻³ M
Then,