Step-by-step explanation:
First, calculate the moles of
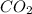 using ideal gas equation as follows.
using ideal gas equation as follows.
PV = nRT
or, n =
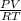
=
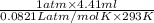 (as 1 bar = 1 atm (approx))
(as 1 bar = 1 atm (approx))
= 0.183 mol
As, Density =
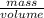
Hence, mass of water will be as follows.
Density =
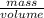
0.998 g/ml =
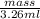
mass = 3.25 g
Similarly, calculate the moles of water as follows.
No. of moles =
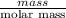
=
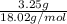
= 0.180 mol
Moles of hydrogen =
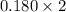 = 0.36 mol
= 0.36 mol
Now, mass of carbon will be as follows.
No. of moles =
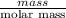
0.183 mol =
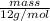
= 2.19 g
Therefore, mass of oxygen will be as follows.
Mass of O = mass of sample - (mass of C + mass of H)
= 3.50 g - (2.19 g + 0.36 g)
= 0.95 g
Therefore, moles of oxygen will be as follows.
No. of moles =
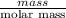
=
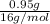
= 0.059 mol
Now, diving number of moles of each element of the compound by smallest no. of moles as follows.
C H O
No. of moles: 0.183 0.36 0.059
On dividing: 3.1 6.1 1
Therefore, empirical formula of the given compound is
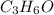 .
.
Thus, we can conclude that empirical formula of the given compound is
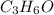 .
.