Answer:
A. 25.5
Step-by-step explanation:
The monopolist's profit function is:
Profit = Price*Q(Price) - marginal cost
Since the marginal cost is $1 for each unit produced, profit is given by:
Profit = Price*Q(Price) - 1*Q(Price)
Since the Q(p) function is given, profits are given by:
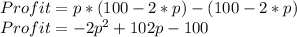
The maximum value for the profit function occurs at the point in which the function's derivative equals zero, therefore:
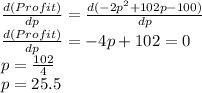
The price that the monopolist will set to maximize its profits is 25.5.