Answer : The value of
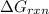 is -49.2 kJ/mol
is -49.2 kJ/mol
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the reaction quotient.
Reaction quotient (Q) : It is defined as the measurement of the relative amounts of products and reactants present during a reaction at a particular time.
The given balanced chemical reaction is,
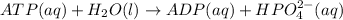
The expression for reaction quotient will be :
![Q=([ADP][HPO_4^(2-)])/([ATP])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/c9y995ymahj8pm8bqwstguejivdqczd0m3.png)
In this expression, only gaseous or aqueous states are includes and pure liquid or solid states are omitted.
Given:
![[ATP]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/yhnd218o8j6m4s62m5569d8fwtiu5nn0q3.png) = 5.0 mM
= 5.0 mM
![[ADP]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/77qtknfbboa4m4n9ek1ljnag1rxvreec3a.png) = 0.70 mM
= 0.70 mM
![[HPO_4^(2-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/t7c4zjgucnoa05itpdcogyuk923t6fwx6n.png) = 5.0 mM
= 5.0 mM
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get
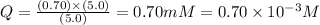
Now we have to calculate the value of
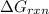 .
.
The formula used for
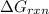 is:
is:
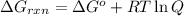 ............(1)
............(1)
where,
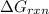 = Gibbs free energy for the reaction = ?
= Gibbs free energy for the reaction = ?
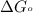 = standard Gibbs free energy = -30.5 kJ/mol
= standard Gibbs free energy = -30.5 kJ/mol
R = gas constant =
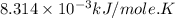
T = temperature =
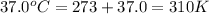
Q = reaction quotient =
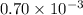
Now put all the given values in the above formula 1, we get:
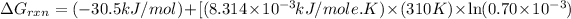
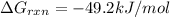
Therefore, the value of
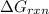 is -49.2 kJ/mol
is -49.2 kJ/mol