Answer:
The order of the decomposition reaction is 2.
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate constant of reaction at 593 K , =
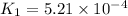
Rate constant of reaction at 673 K , =
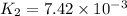
Rate of the reaction at 593 K =
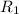
Initial concentration of reactant = [A] = 0.2264 M
![R_1=K_1* [A]^x](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/g2joqwhpa5txjwq180i5d4e6bprcti6thp.png)
![R_1=5.21* 10^(-4)* [A]^x](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/r72yr9nmcn6xhqx5uyilzw9ffjmtia9kn1.png) ...[1]
...[1]
Rate of the reaction at 673 K =
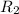
Initial concentration of reactant = [A'] = 0.05999 M
![R_2=K_2* [A']^x](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/m06zsliz5c7o624o7tfzt2k147qgltbp4x.png)
![R_2=7.42* 10^(-3)* [A']^x](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/y0lypykq4s3my4rkezaluch108wteqhc5b.png) ...[2]
...[2]
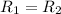 (given)
(given)
![5.21* 10^(-4)* [A]^x=7.42* 10^(-3)* [A']^x](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/9bpgejv856kcpixcgdsb4o4wpv7jskgvar.png)
![(([A])/([A']))^x=(7.42* 10^(-3))/(5.21* 10^(-4))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/emw7of4q9agssn5lbkur6tryznobu6wso9.png)
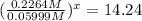
x = 1.999 ≈ 2
The order of the decomposition reaction is 2.