Answer:
The magnitude of the field is 1.112 T
The direction in case of proton is
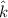 , i.e., outwards
, i.e., outwards
The direction in case of proton is
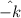 , i.e., inwards
, i.e., inwards
Solution:
As per the question:
Velocity of the proton,
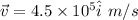
Magnetic force,
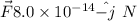
Charge on proton, q =
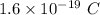
Charge on electron, e =
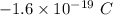
Now,
The magnitude of the mgnetic field can be given by the formula of Lorentz force:
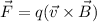
For maximum force, the magnitude of the force is given by:
F = qvB
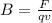
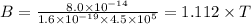
Now, for the direction of the field:
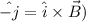
The direction that we get from the above eqn is
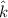
Now, in case of electron:
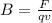
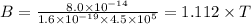
Now, for the direction of the field:
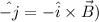
The direction that we get from the above eqn is
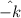 , i.e., directed inwards.
, i.e., directed inwards.