Step-by-step explanation:
1) Henry's law states that the amount of gas dissolved or molar solubility of gas is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the liquid.
To calculate the molar solubility, we use the equation given by Henry's law, which is:
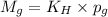
where,
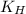 = Henry's constant
= Henry's constant
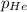 = partial pressure of gas
= partial pressure of gas
a)
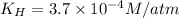
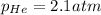
Putting values in above equation, we get:
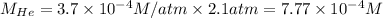
The solubility of helium gas is
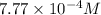
b)
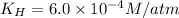
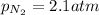
Putting values in above equation, we get:
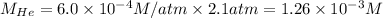
The solubility of nitrogen gas is
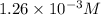
2)
a) Mass of solute or methanol , m= 14.7 g
Mass of solvent or water , m'= 186 g
Mass of the solution = M = m + m' = 14.7 g + 186 g = 200.7 g
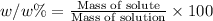
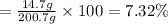
The mass percent of methanol is 7.32%.
b) Molality is defined as moles of solute per kilograms of solvent.
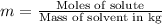
Moles of methanol =
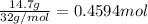
Mass of solvent = 186 g = 0.186 kg
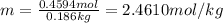
The molality of methanol is 2.4610 mol/kg.