To solve this exercise, it is necessary to apply the concepts of conservation of the moment especially in objects that experience an inelastic colposition.
They are expressed as,
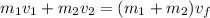
Where,
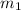 = mass of the skier
= mass of the skier
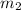 = mass of the cat
= mass of the cat
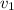 = initial velocity of skier
= initial velocity of skier
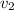 = initial velocity of cat
= initial velocity of cat
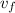 = final velocity of both
= final velocity of both
Re-arrange to find V_f we have,
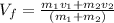
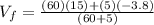
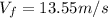
Once the final velocity is found it is possible to calculate the change in kinetic energy, so
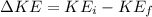
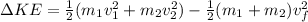
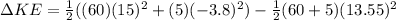
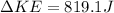
Therefore the amount of kinetic energy converted in to internal energy is 819J