Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
l = 5 mm =
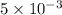 m, A = 0.5
m, A = 0.5
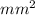 =
=
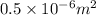
conductivity (
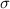 ) =
) =
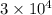 per ohm-m
per ohm-m
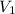 = 13 volts,
= 13 volts,
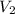 = 17 volts
= 17 volts
Now, the relation between conductivity and resistivity is as follows.
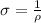
where,
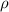 = resistivity
= resistivity
Therefore, calculate resistivity as follows.
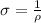
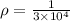
=
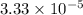 ohm-m
ohm-m
Now, we will calculate the resistance using the following formula.
R =
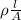
=
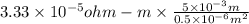
= 0.333 ohm
Hence, value of resistance is 0.333 ohm.
As we know that relation between current and voltage is as follows.
V = IR
Therefore, calculate the value of current as follows.
V = IR
(17 - 13) =
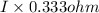
I = 12.01 ampere
Thus, value of the current is 12.01 A.