Answer: unfavourable, unfavourable, non spontaneous
Step-by-step explanation:
Endothermic reactions are those in which heat is absorbed by the system and exothermic reactions are those in which heat is released by the system.
 for Endothermic reaction is positive and
for Endothermic reaction is positive and
 for Exothermic reaction is negative.
for Exothermic reaction is negative.
Entropy is the measure of randomness or disorder of a system. If a system moves from an ordered arrangement to a disordered arrangement, the entropy is said to decrease and vice versa.
For the reaction:
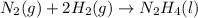
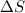 is negative as the randomness decreases when gases convert into liquid.
is negative as the randomness decreases when gases convert into liquid.
For reaction to be spontaneous,
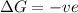 and favourable conditions are
and favourable conditions are
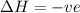 and
and
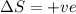
Using Gibbs Helmholtz equation:
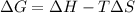
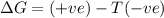
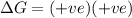
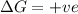
Thus the reaction is non spontaneous at all temperatures.