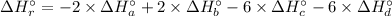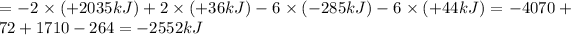Answer:
(A)
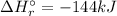
(B)
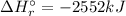
Step-by-step explanation:
(A) 2NO(g) + O₂(g) → 2NO₂(g)
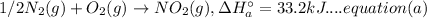
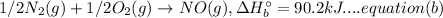
Now, multiplying equation (a) with 2:
⇒
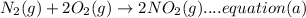
Then equation b is reversed and multiplied with 2:
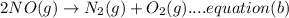
Now by adding the equation (a) and equation (b), we get:
⇒
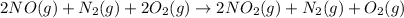
⇒ 2NO(g) + O₂(g) → 2NO₂(g)
Therefore, the enthalpy of the reaction:
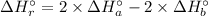
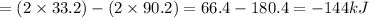
(B) 4B(s)+3O₂(g) → 2B₂O₃(s)
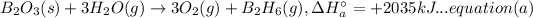
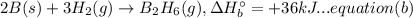
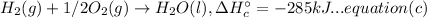
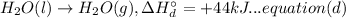
Now multiplying equation (b) with 2, reversing equation (a) and multiplying with 2. Reversing equation (c) and (d) and multiplying both with 6.
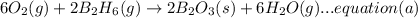
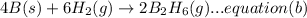
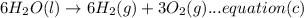
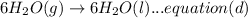
Now by adding the equations (a), (b), (c), (d); we get:
4B(s)+3O₂(g) → 2B₂O₃(s)
Therefore, the enthalpy of the reaction: