Answer:
The final molarity of chloride anion in the solution is 0 molar.
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass of potassium chloride solution = 1.88 g
Moles of potassium chloride =
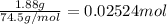
Moles of silver nitrate = n
Molarity of silver nitrate solution = M= 23.0 M
Volume of the silver nitrate solution ,V= 300.0 mL = 0.3 L
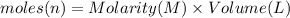
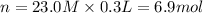
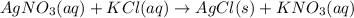
According to reaction 1 mol of potassium nitrate reacts with 1 mol of silver nitrate .
Then 0.02524 moles of potassium chloride will react with:
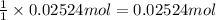 of silver nitrate.
of silver nitrate.
As we can see that potassium chloride is in limiting amount due to which the potassium chloride will get completely converted into silver chloride and potassium nitrate.
Since , no potassium chloride will left after reaction which indicates that no chloride ions will be present after reaction.
![[Cl^-]=0 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/vk9e013d8aduir0059hlgeq8eaagy9j1hd.png)
The final molarity of chloride anion in the solution is 0 molar.