Answer: a.
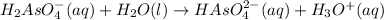
b.
![K_a=([HAsO_4^(2-)]* [H_3O^+])/([H_2AsO_4^(-)])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/uwnwo6avctvlej847wmcixx4ggmpjqzf5r.png)
Explanation:-
According to the Bronsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base theory, an acid is defined as a substance which looses donates protons and thus forming conjugate base and a base is defined as a substance which accepts protons and thus forming conjugate acid.
The balanced chemical equation is:
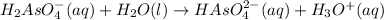
Here,
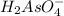 is loosing a proton, thus it is considered as an acid and after losing a proton, it forms
is loosing a proton, thus it is considered as an acid and after losing a proton, it forms
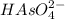 which is a conjugate base.
which is a conjugate base.
And,
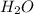 is gaining a proton, thus it is considered as a base and after gaining a proton, it forms
is gaining a proton, thus it is considered as a base and after gaining a proton, it forms
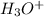 which is a conjugate acid.
which is a conjugate acid.
The dissociation constant is given by:
![K_a=([HAsO_4^(2-)]* [H_3O^+])/([H_2AsO_4^-])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/z46h530ger9oggnorvddz2dge9q5tr777u.png)