Answer: The potential of the given cell is 0.856 V
Step-by-step explanation:
The substance having highest positive
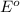 potential will always get reduced.
potential will always get reduced.
Half reactions for the given cell follows:
Oxidation half reaction:
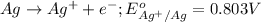 ( × 2)
( × 2)
Reduction half reaction:
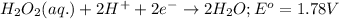
Net reaction:
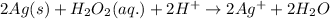
Oxidation reaction occurs at anode and reduction reaction occurs at cathode.
To calculate the
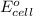 of the reaction, we use the equation:
of the reaction, we use the equation:
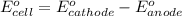
Putting values in above equation, we get:
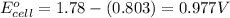
To calculate the EMF of the cell, we use the Nernst equation, which is:
![E_(cell)=E^o_(cell)-(2.303RT)/(nF)\log ([Ag^(+)]^2)/([H^(+)]^2[H_2O_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ajebz1y2m7f58wedzs2s7ya767ejris9oz.png)
where,
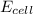 = electrode potential of the cell = ?V
= electrode potential of the cell = ?V
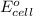 = standard electrode potential of the cell = +0.977 V
= standard electrode potential of the cell = +0.977 V
R = Gas constant = 8.314 J/K mol
T = temperature = 279 K
F = Faraday's constant = 96500 C
n = number of electrons exchanged = 2
![[Ag^(+)]=0.559M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/i66kh3z05mn8x17fvgpxsbxy18o109o8eu.png)
![[H^(+)]=0.00393M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/dyx6ry3hyn7qxp4nhixylbrbfmueya30u3.png)
![[H_2O_2]=0.863M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/l0xff1lcnxugzk2m921owitbr9yr3kfkda.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
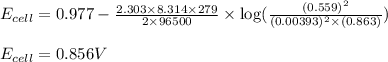
Hence, the potential of the given cell is 0.856 V