Answer:
1. 0.071 atm
2. 0.018 atm
3. 0.089 atm
4. 0.070 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
4HCl(g)+O₂(g) → 2Cl₂(g)+2H₂O(g)
1. First we calculate the moles of HCl and then we use PV=nRT to calculate P:
- 0.460gCl₂ ÷ 70.9g/1molCl₂ *
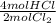 = 0.0130 mol HCl
= 0.0130 mol HCl
- P * 5.70 L = 0.0130 mol * 0.082 atm·Lmol⁻¹·K⁻¹ * 379.96 K
2. We do the same but with O₂
- 0.460gCl₂ ÷ 70.9g/1molCl₂ *
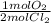 = 3.244x10⁻³mol O₂
= 3.244x10⁻³mol O₂
- P * 5.70 L =3.244x10⁻³mol * 0.082 atm·Lmol⁻¹·K⁻¹ * 379.96 K
3. The total pressure is the sum of the pressures of all components. Before the reaction took place, there are only reactants:
- P = 0.071 atm + 0.018 atm = 0.089 atm
4. After the reaction went to completion, there are only products, because stoichiometric amounts of reactants were used.
So now we calculate the pressure of Cl₂ and of H₂O:
- Cl₂ ⇒ 0.460gCl₂ ÷ 70.9g/1molCl₂ = 6.488x10⁻³ molCl₂
- P * 5.70 L =6.488x10⁻³mol * 0.082 atm·Lmol⁻¹·K⁻¹ * 379.96 K
P = 0.035 atm
- H₂O ⇒ 0.460gCl₂ ÷ 70.9g/1molCl₂ *
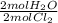 = 6.488x10⁻³ molH₂O
= 6.488x10⁻³ molH₂O
- P * 5.70 L =6.488x10⁻³mol * 0.082 atm·Lmol⁻¹·K⁻¹ * 379.96 K
P = 0.035 atm
The total pressure thus is:
- P = 0.035 atm + 0.035 atm = 0.070 atm